HOMOEOPATHY FOR ONYCHOLYSIS
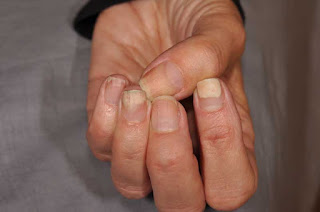
Onycholysis is the painless separation of the nail from the nail bed. Onycholysis occurs when the nail separates from the nail bed or the skin directly beneath the nail. There are several possible causes for this common condition. Onycholysis can last for several months and will typically correct itself when the nail fully grows out. Until then, the nail will not reattach to the skin beneath it. Recovery time varies for onycholysis as it is largely dependent on nail growth. It is not uncommon for fingernails to take about 4 to 6 months to grow to a full size. Toenails may take up to 8 months. Onycholysis can affect multiple units or a single nail unit. If multiple nail units are affected , a systemic cause is a more likely culprit. If a single nail unit is affected , a history of trauma can often be elicited in the clinical history. Causes The cause of a person's onycholysis varies widely. A person may experience an injury or repetitive trauma. · Simply t



